Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Training and Certification is a practitioner-level programme designed for professionals who are expected to lead defined improvement projects and deliver measurable performance improvement within their area of responsibility.
The programme builds a strong working foundation in Lean and Six Sigma principles and applies them through the Define–Measure–Analyse–Improve–Control (DMAIC) framework. You develop the capability to scope improvement opportunities, analyse process performance, use data to support decisions, manage change locally and implement improvements that deliver sustainable results.
All course content, learning resources, assessments and exams are supported with multilingual language capability, enabling participants to learn, collaborate and apply tools effectively across global and cross-functional environments.
By completing the Green Belt, you return to work equipped to lead structured improvement projects end-to-end, contribute confidently to organisational performance goals and support the development of a continuous improvement culture within your team or function.
How you benefit
![]() Lead structured Lean Six Sigma improvement projects using the DMAIC framework
Lead structured Lean Six Sigma improvement projects using the DMAIC framework![]() Apply practical tools to improve quality, efficiency, cost and customer experience
Apply practical tools to improve quality, efficiency, cost and customer experience![]() Use data and analysis to diagnose problems and make confident decisions
Use data and analysis to diagnose problems and make confident decisions![]() Identify waste, manage variation and address root causes of performance gaps
Identify waste, manage variation and address root causes of performance gaps![]() Build the capability to sustain improvements within your team or function
Build the capability to sustain improvements within your team or function
Participant Profile
This Green Belt programme is suited to professionals from manufacturing, service and transactional environments, including team members, supervisors, project and change managers, functional specialists, consultants and leaders who are expected to contribute to or lead improvement initiatives. Group and team participation is supported, including action learning projects aligned to organisational priorities.
Course Pre-requisites
An interest in developing practitioner-level continuous improvement capability.
Exam and Certification
Online multiple-choice exam
30 questions
40 minutes
Pass mark: 70%
Successful completion results in Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification.
This format is designed for professionals who value immersive, in-person learning and want dedicated time away from day-to-day work to focus fully on developing their Lean Six Sigma capability. Delivered in a public classroom setting, the course combines expert instruction, practical exercises and peer learning to accelerate understanding and confidence.
Across five consecutive days, you will work closely with a Master Black Belt instructor and a cohort of professionals from different organisations and sectors. Concepts are introduced, explored and applied in real time, with continuous opportunity to ask questions, test ideas and learn from the experiences of others in the room.
The classroom environment supports deep learning through facilitated discussion, group problem-solving and hands-on application of tools. You will work through the DMAIC methodology step by step, using real-world examples and case material to ensure concepts translate directly back into your workplace.
By the end of the week, you leave with a strong practical grasp of Lean Six Sigma tools, a clear understanding of how to apply them, and the confidence to lead improvement initiatives in your organisation.
Spend five focused days working intensively with a Master Black Belt and a small cohort of professionals from different organisations. Sessions are highly interactive, combining short teaching inputs with discussion, group exercises and hands-on application to keep energy and engagement high throughout the week.
Learning is driven by collaboration and challenge. You will explore concepts together, test ideas in real time and benefit from continuous feedback from both the instructor and your peers. The diversity of experience in the room brings different perspectives to common improvement challenges and deepens understanding.
Throughout the programme, emphasis is placed on practical application rather than theory alone. Tools and techniques are explored in a way that makes it clear how they are used in real organisations, helping you leave with a clear sense of how to apply what you have learned to improvement work back in your role.
Curriculum and Course Format
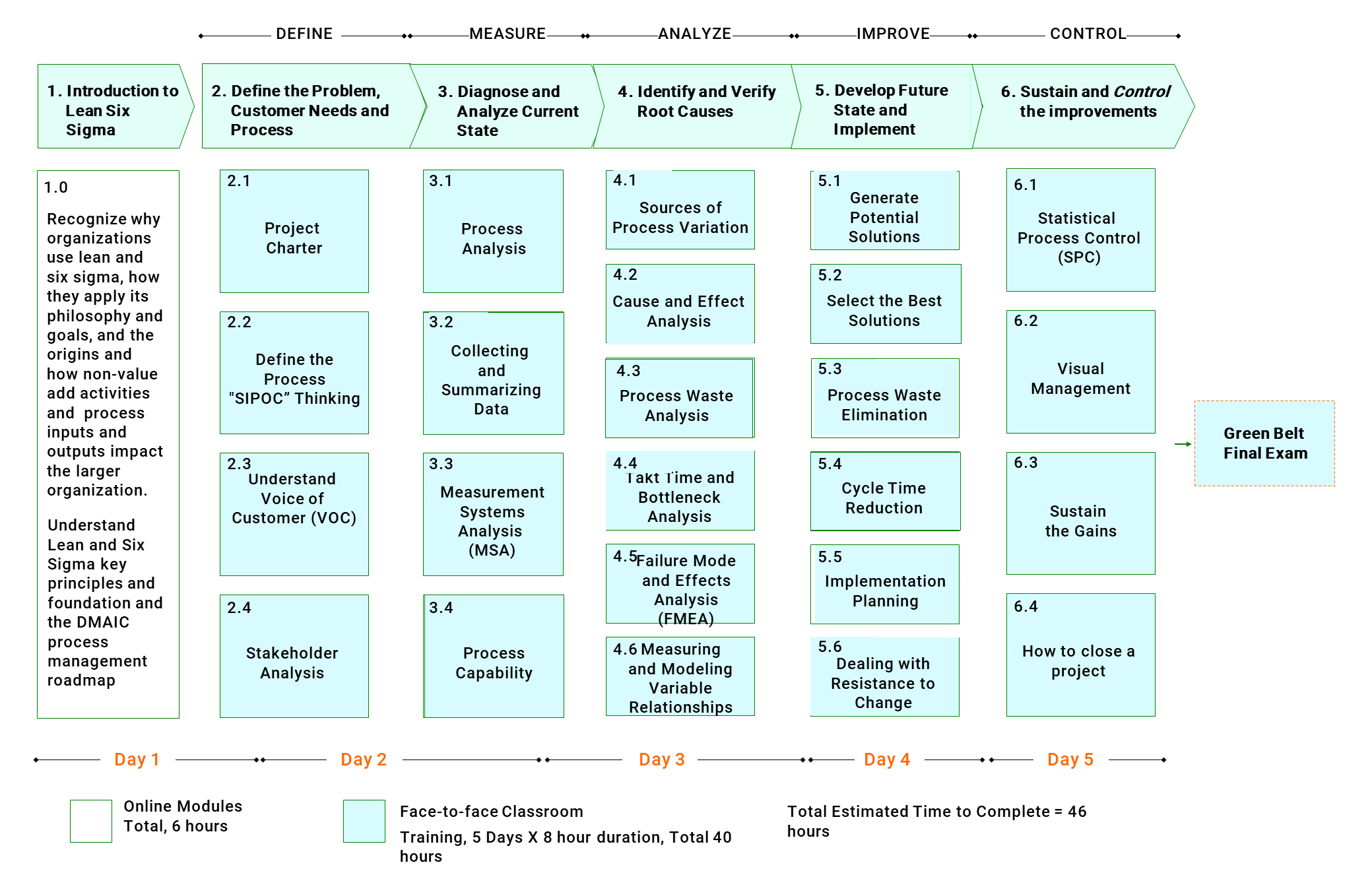
1.0 INTRODUCTION TO LEAN SIX SIGMA
Understand the value of lean and six sigma, its philosophy, history and goals and the rationale for combining the lean and six sigma approaches to apply to improvement projects.
Understand lean six sigma principles and foundation and the Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control (DMAIC) process management roadmap.
Understand how non-value add activities and process inputs and outputs impact the larger organization.
1.01 Six Sigma DMAIC Overview
1.02 Process Variation
1.03 Six Sigma and Organizational Goals
1.04 The DMAIC Process Management Roadmap
1.05 Belt Structure for Skills Development
1.06 Summary – Six Sigma DMAIC Overview
1.07 Introduction to Lean
1.08 The Origin of Lean
1.09 Foundations of Lean
1.10 Value-add and Non-value-add Activities
1.11 Lean Mindset and Thinking
1.12 Summary – Introduction to Lean
1.13 Integration of Lean and Six Sigma to drive On- Time, On-Quality and On Cost performance
2.0 DEFINE
Define the scope and goals of the improvement project in terms of customer and/or business requirements, the process that delivers these requirements and stakeholder needs.
2.01 Overview – Define Phase
2.02 Problem Definition and Project Charter
2.03 Define the Process – SIPOC Thinking
2.04 Understand Voice of Customer (VOC)
2.05 Customer Identification
2.06 Gather Customer Feedback
2.07 Analyze VOC Data
2.08 Define What is Critical to Quality (CTQ)
2.09 Summary – Understand Voice of Customer (VOC)
2.10 Stakeholder Analysis
2.11 Summary – Define Phase
3.0 MEASURE
Map the process and measure, understand and baseline the current process performance and capability through a set of relevant and robust measures.
Calculate process performance metrics such as defects per unit (DPU), rolled throughput yield (RTY), cost of poor quality (COPQ), defects per million opportunities (DPMO) sigma levels and process capability indices.
3.01 Overview – Measure Phase
3.02 Process Analysis
3.03 Collecting and Summarizing Data
3.04 Types of Data and Measurement Scales
3.05 Evaluating Metrics
3.06 Data Collection Methods
3.07 Sampling Methods
3.08 Descriptive Statistics
3.09 Graphical Techniques
3.10 Summary – Collecting and Summarizing Data
3.11 Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA)
3.12 Process Capability
3.13 Process Capability Indices
3.14 Process Performance Indices
3.15 Short-term and Long-term Capability
3.16 Process Capability for Attribute data
3.17 Process Performance vs. Specification
3.18 Summary – Process Capability
3.19 Summary – Measure Phase
4.0 ANALYZE
Analyze the gap between the current and desired performance, prioritise problems, process risk and identify root causes and understand / statistically verify their effect on process performance.
4.01 Overview – Analyze Phase
4.02 Sources of Process Variation
4.03 Cause and Effect Analysis
4.04 Process Waste Analysis
4.05 Takt Time and Bottleneck Analysis
4.06 Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
4.07 Measuring and Modeling Variable Relationships
4.08 Input and Output Variables
4.09 Correlation
4.10 Regression
4.11 Summary – Measuring and Modeling Variable Relationships
4.12 Summary – Analyze Phase
5.0 IMPROVE
Generate, select and implement improvement solutions to fix the problems and prevent them from re-occurring so that the required performance goals are met.
Use concepts such as value chain, flow, pull, perfection, etc., and tools commonly used to eliminate waste, including kaizen, 5S, A3 problem solving, morning meetings etc.
5.01 Overview – Improve Phase
5.02 Generate Potential Solutions
5.03 Select the Best Solutions
5.04 Process Waste Elimination
5.05 Cycle Time Reduction
5.06 Implementation Planning
5.07 Dealing with Resistance to Change
5.08 Summary – Improve Phase
6.0 CONTROL
Implement the improved process / solutions in a way that sustains and “holds the gains “and the process has robust control measures and a response plan.
The objectives and benefits of statistical process control (SPC) to track process performance and identify special and common causes.
6.01 Overview – Control Phase
6.02 Sustain the Gains
6.03 Documentation
6.04 Monitor Performance
6.05 Lessons Learned
6.06 Visual Management
6.07 Statistical Process Control (SPC)
6.08 How to close a project
6.09 Summary – Control Phase
Quizzes Segmented and embedded during and at the end of each DMAIC Phase
Final Exam Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Certification
Next Course Dates
E-Learning Modules
6 Hours
Face-to-Face Classroom Training 5 Day x 8 Hours
40 Hours
United Kingdom
13 – 17th April 2026
This course is delivered in partnership with Norwich Business School
- 23 – 27th March 2026
Estimated time to complete
46 Hours
Course Fee (excluding VAT)
£ 2,395
What's Included
- Five days of face-to-face, instructor-led Green Belt training
- 12 months access to the Green Belt Bootcamp platform, including toolkits, case studies and downloadable resources
- Green Belt online exam and electronic certificate
- Unlimited practice exams and free resits
- Tutor support via discussion groups and messaging
- Access to a global Lean Six Sigma learning community
The quickest, easiest and most engaging way for individuals and companies to get on track with Lean Six Sigma concepts and tools.
In-person and virtual workshops
Ready-to-use job aids, tools and templates
Peer-to-peer learning forums
Distinctive digital learning content
Expert coaching support
Nudges, reminders and micro learning
Excellent for remote teams
Auto-translate curriculum and instruction
Multi-channel; eLearning, virtual, face-to-face or in-house
Make progress in less time and deliver results quickly
Tailored learning solutions for companies
Mobile friendly
Highly practical
Join our Lean Six Sigma community
Practice exams
World Class Lean Six Sigma Certification