Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Training
Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Training and Certification is an advanced practitioner programme designed for experienced professionals who are expected to lead complex improvement initiatives and drive sustained performance change across teams, functions and processes.
Building on prior Green Belt knowledge, the programme develops deeper analytical capability, stronger change leadership skills and the confidence to address more complex, cross-functional challenges. You extend your ability to diagnose performance issues, evaluate improvement options and apply advanced tools and techniques in a range of real organisational scenarios.
For participants who completed Green Belt training some time ago, refresher modules are included to reinforce core concepts and close any gaps in knowledge, ensuring a strong and consistent foundation before progressing.
Advanced analysis is supported through the use of statistical software, including a Minitab trial version, with clear guidance provided upon enrolment so you are fully prepared to use the tools effectively during the programme.
All course content, learning resources, assessments and exams are supported with multilingual language capability, enabling participants to learn, collaborate and apply learning effectively across global and cross-functional environments.
By completing the Black Belt, you return to work equipped to lead high-impact improvement projects, manage resistance to change, coach others through structured problem-solving and contribute at a more strategic level to organisational improvement efforts.
How you benefit
![]() Lead complex, cross-functional Lean Six Sigma improvement initiatives using advanced DMAIC application
Lead complex, cross-functional Lean Six Sigma improvement initiatives using advanced DMAIC application![]() Apply advanced analytical and statistical tools to diagnose and validate performance issues
Apply advanced analytical and statistical tools to diagnose and validate performance issues![]() Drive sustainable improvement through structured change leadership and stakeholder engagement
Drive sustainable improvement through structured change leadership and stakeholder engagement![]() Coach and support Green Belts and project teams to improve delivery capability
Coach and support Green Belts and project teams to improve delivery capability![]() Translate data, analysis and insight into actionable business decisions
Translate data, analysis and insight into actionable business decisions
Participant Profile:
This Black Belt programme is suited to experienced improvement practitioners from manufacturing, service and transactional environments, including senior project and change managers, operational leaders, improvement specialists and consultants who are responsible for leading complex initiatives and influencing performance beyond a single team or function.
Participants are typically expected to take ownership of high-impact improvement work, support other practitioners and contribute to the wider deployment of continuous improvement capability within their organisation.
Course Pre-requisites
Prior Lean Six Sigma Green Belt certification or equivalent experience is required.
Exam and Certification
Online multiple-choice exam
50 questions
70 minutes
Pass mark: 70%
Successful completion results in Lean Six Sigma Black Belt certification.
The Black Belt Virtual Classroom is designed for experienced Lean Six Sigma practitioners leading complex, cross-functional improvement and change initiatives. It combines advanced, instructor-led learning with the flexibility of remote delivery, without compromising rigour, challenge or depth.
Delivered live by an experienced Master Black Belt, the programme runs through a structured series of interactive virtual workshops. Sessions are carefully paced to ensure advanced concepts are understood, challenged and applied, with time between workshops to analyse data and begin applying learning to real improvement work.
Unlike self-paced learning, this format creates a shared, high-level learning environment. You learn alongside other experienced professionals, engage in critical discussion, challenge assumptions and benefit from facilitator insight drawn from complex, real-world transformation programmes.
Learning is delivered through live, instructor-led virtual workshops supported by structured preparation and ongoing access to the Black Belt Bootcamp platform. Core tools and techniques are introduced progressively, allowing workshop time to focus on interpretation, application and decision-making rather than theory alone.
This approach supports deeper analytical thinking while giving you the space to work with real data, real processes and real organisational constraints.
Learning is brought to life through three instructor-led virtual workshops, each six hours in duration, delivered by an experienced Master Black Belt. These live sessions are tightly integrated with the online preparation, ensuring a clear connection between what you study independently and how you apply it in practice.
The virtual workshops are highly interactive and collaborative. You work alongside other experienced practitioners, drawing on real challenges and examples to deepen understanding and sharpen judgement.
During the live sessions, you will:
- Consolidate and extend your understanding of advanced concepts
- Share experience and insight with peers from different organisations
- Be challenged and coached by a Master Black Belt instructor
Apply tools and techniques to realistic, complex case scenarios
At Black Belt level, the focus shifts from applying tools to making sound judgements in complex, uncertain environments. The programme develops your ability to interpret data critically, validate conclusions and select the right analytical approach when trade-offs, risk and organisational constraints are involved. Through live challenge from the Master Black Belt, peer debate and worked examples, you strengthen how you think, not just what you calculate.
As the course progresses, you apply advanced analysis to real improvement scenarios, building the confidence to lead high-impact, cross-functional initiatives, influence stakeholders and manage resistance to change. By the end of the programme, you are equipped to use Lean Six Sigma thinking at both operational and strategic levels, translating insight into decisions that drive sustained performance improvement.
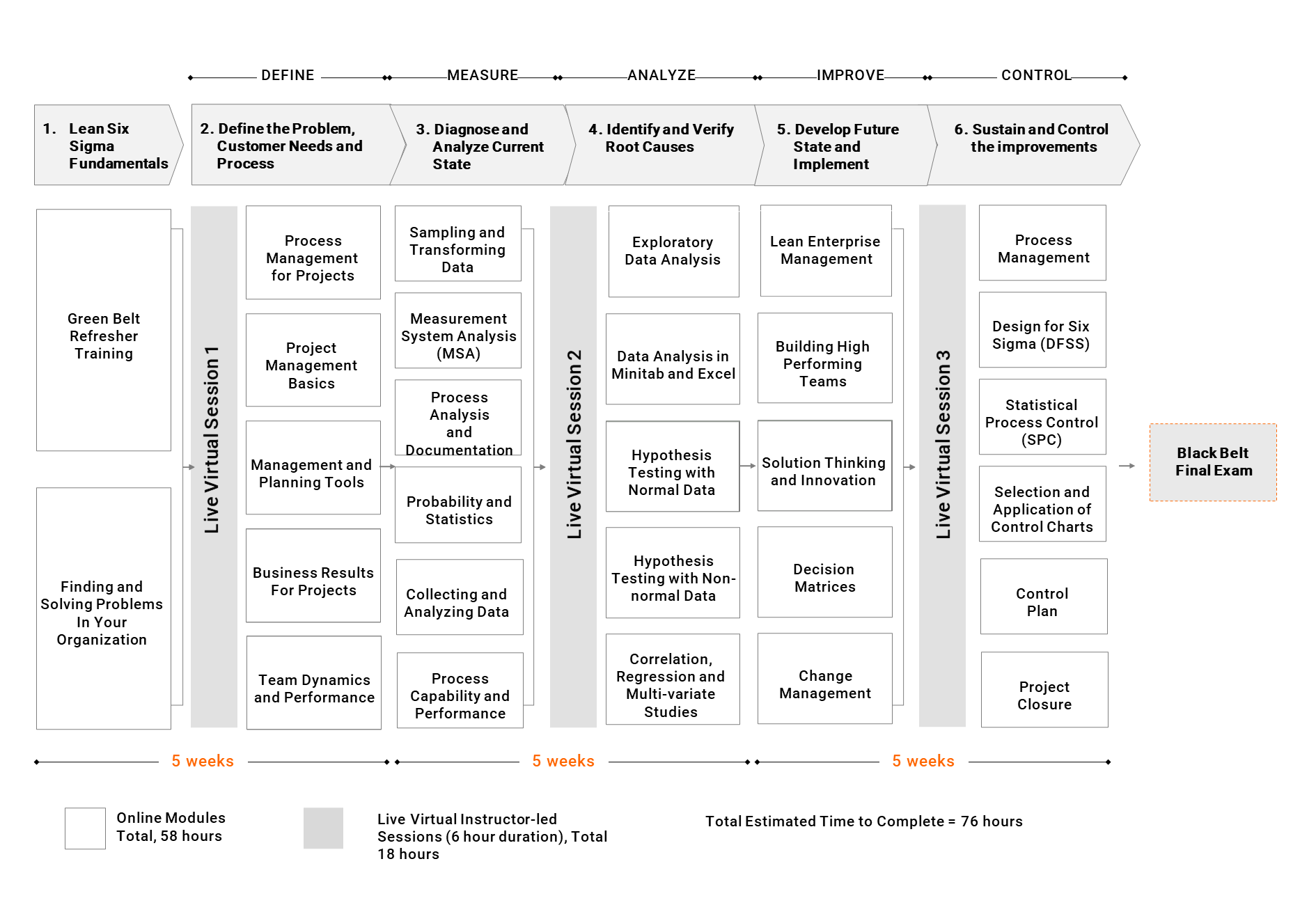
1.0 INTRODUCTION
4 Hours
Understand how lean and six sigma tools are applied to improve all types of processes in all types of enterprises: manufacturing, service, transactional, product and process design, innovation, etc.
Recognize key drivers for business (profit, market share, customer satisfaction, efficiency, product differentiation) and how key metrics and scorecards are developed and impact the entire organization.
1.1 Green Belt Refresher Training
1.2 Finding and Solving Problems in your Organisation
2.0 DEFINE
6 Hours
Define the scope and goals of the improvement project in terms of customer and/or business requirements, the process that delivers these requirements and stakeholder needs
2.2.1 |
Process elements |
2.2.2 |
Owners and stakeholders |
2.2.3 |
Identify customers |
2.3.1 | Collect customer data |
2.3.2 | Analyze customer data |
2.3.3 | Translate customer requirements |
2.4.1 | Building a Business Case & Project Charter |
2.4.2 | Project scope |
2.4.3 | Project metrics |
2.4.4 | Project planning tools |
2.4.5 | Project documentation |
2.4.6 | Project risk analysis |
2.4.7 | Project closure |
2.6.1 | Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) |
2.7.1 | Team stages and dynamics |
2.7.2 | Six sigma and other team roles and responsibilities |
2.7.3 | Team tools |
2.7.4 | Communication |
3.0 MEASURE
14 Hours
Calculate and interpret measures of dispersion and central tendency and construct and interpret frequency distributions.
Define and apply the concepts related to sampling (e.g., representative selection, homogeneity, bias, etc.) and select and use appropriate sampling methods (e.g., random sampling, stratified sampling, systematic sampling, etc.) that ensure the integrity of data. data.
Use various analytical methods (e.g., repeatability and reproducibility (R&R), correlation, bias, linearity, precision to tolerance, percent agreement, etc.) to analyze and interpret measurement system capability for variable and attribute measurement systems. Map the process and measure, understand and baseline the current process performance and capability through a set of relevant and robust measures.
Calculate process performance metrics such as defects per unit (DPU), rolled throughput yield (RTY), cost of poor quality (COPQ), defects per million opportunities (DPMO) sigma levels and process capability indices.
3.2.1 | Normality (Central Limit Theorem, P-values, Transforming Data) |
3.2.2 | Sampling Methods (Random and Process Sampling, Determining Sample Sizes, Selecting Samples) |
3.2.3 | EWMA Chart |
3.3.1 | Precision & Accuracy |
3.3.2 | Bias, Linearity & Stability |
3.3.3 | Gauge Repeatability & Reproducibility |
3.3.4 | Variable MSA |
3.4.1 | Process modeling |
3.4.2 | Process inputs and outputs |
3.5.1 | Drawing valid statistical conclusions |
3.5.2 | Central limit theorem and sampling distribution of the mean |
3.5.3 | Basic probability concepts |
| 3.6.1 | Types of data and measurement scales |
| 3.6.2 | Data collection methods |
| 3.6.3 | Techniques for assuring data accuracy and integrity |
| 3.6.4 | Descriptive statistics |
| 3.6.5 | Graphical methods |
| 3.6.6 | Probability distributions |
| 3.6.7 | Measurement System Capability |
distributions
3.6.7 Measurement System Capability
3.7.1 | Process capability studies |
3.7.2 | Process performance vs. specification |
3.7.3 | Process capability indices |
3.7.4 | Process performance indices |
3.7.5 | Short-term vs. long-term capability |
3.7.6 | Process capability for attributes data |
4.0 ANALYZE
10 Hours
Drawing valid statistical conclusions by distinguishing between descriptive and inferential studies and population and sample statistics.
Measuring and modelling relationships between variables to set-up and run hypothesis tests and correlation and regression analysis.
4.2.1 | Classes of Distributions |
4.2.2 | Inferential Statistics |
4.2.3 | Understanding Inference |
4.2.4 | Sampling techniques & uses |
4.2.5 | Central Limit Theorem and the principal correlations |
4.2.6 | Data Transformation, Box Cox |
4.4.1 | General Concepts & Goals of Hypothesis Testing |
4.4.2 | Significance; Practical vs. Statistical |
4.4.3 | Risk; Alpha & Beta |
4.4.4 | Hypothesis Testing of Means, Variances and Proportions ( Z- , p- and t-tests) |
4.4.5 | 1 & 2 sample t-tests |
4.4.6 | 1 sample variance |
4.4.7 | Paired-comparison tests |
4.4.8 | Single-factor analysis of variance (ANOVA) |
4.4.9 | Tests of Equal Variances. Including Tests of Equal Variance, Normality Testing and Sample Size calculation, performing tests and interpreting results. |
4.5.1 | Mann-Whitney |
4.5.2 | Kruskal-Wallis |
4.5.3 | Mood’s Median |
4.5.4 | Sample Sign |
4.5.5 | Sample Wilcoxon |
4.5.6 | One and Two Sample Proportion |
4.5.7 | Chi-Squared (Contingency Tables)a. Including Tests of Equal Variance, Normality Testing and Sample Size calculation, performing tests and interpreting results. |
4.6.1 | Simple linear correlation and regression |
4.6.1 | Simple linear correlation and regression |
5.0 IMPROVE
8.5 Hours
Apply divergent thinking by using creativity techniques to identify innovative solutions.
Use various tools and techniques for reducing cycle time, including continuous flow, single-minute exchange of die (SMED), etc.
How to make data driven project decisions Build High Performing Teams for project success How to Manage Resistance to Change
5.2.1 | Pull: Takt Time and Line Balancing, Kanban, Supermarket |
5.2.2 | Flow: Batch Reduction, Parallel Processing, Standard Work & Multi skilling, Modular Design, Layout & Cells, Quick Changeover (SMED), Level Scheduling |
5.2.3 | Steps to Perfection, Operational Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), Bottlenecks, Total Productive/Preventative Maintenance (TPM) |
5.2.4 | Assumption Busting the status quo |
6.0 CONTROL
9.5 Hours
Application of Six Sigma Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) Methodology to drive growth through innovation. Application of statistical process control (SPC) including control chart selection for monitoring and controlling process performance, tracking trends, runs and identifying special and common causes using rules for determining statistical control. Develop a Control Plan to emmbed Process Management principles
6.4.1 | Objectives and benefits |
6.4.2 | Rational subgrouping |
6.5.1 | −R, |
6.5.2 | −s, individuals and moving range (ImR / XmR), median |
6.5.3 | p, np, c, and u chart |
6.5.4 | Analysis of control charts |
Quizzes Segmented and embedded during and at the end of each DMAIC Phase
5 hours
Final Exam Lean Six Sigma Black Belt Certification
1 hours
Total Estimated Time to Complete Black Belt Training & Certification:
58 hours
Next Course
E-Learning Modules
58 Hours
Instructor-led Live Virtual Sessions
18 Hours
Dates
17th Feb 2026
24th Feb 2026
3rd Mar 2026
Virtual Instructor-led sessions take place live via Zoom between 09:30 to 15:30 BST / 08.30 to 14:30 UTC
Estimated time to complete
76 Hours
Course Duration
15 Weeks
Course Fee
£ 2,195
What's Included
- Live, instructor-led Black Belt Virtual Classroom delivered by a Master Black Belt
- Three interactive virtual workshops, six hours each
- 12 months access to the Black Belt Bootcamp platform, including advanced tools, case studies and resources
- Green Belt refresher modules to close any knowledge gaps before progressing
- Black Belt online exam and electronic certificate
- Tutor support and peer discussion via the Bootcamp platform
- Access to a global community of experienced Lean Six Sigma practitioners
The quickest, easiest and most engaging way for individuals and companies to get on track with Lean Six Sigma concepts and tools.
In-person and virtual workshops
Ready-to-use job aids, tools and templates
Peer-to-peer learning forums
Distinctive digital learning content
Expert coaching support
Nudges, reminders and micro learning
Excellent for remote teams
Auto-translate curriculum and instruction
Multi-channel; eLearning, virtual, face-to-face or in-house
Make progress in less time and deliver results quickly
Tailored learning solutions for companies
Mobile friendly
Highly practical
Join our Lean Six Sigma community
Practice exams
World Class Lean Six Sigma Certification